Electric Fuse – Understanding the Science of Circuit Protection
Class: class 10 science
What is an Electric Fuse?
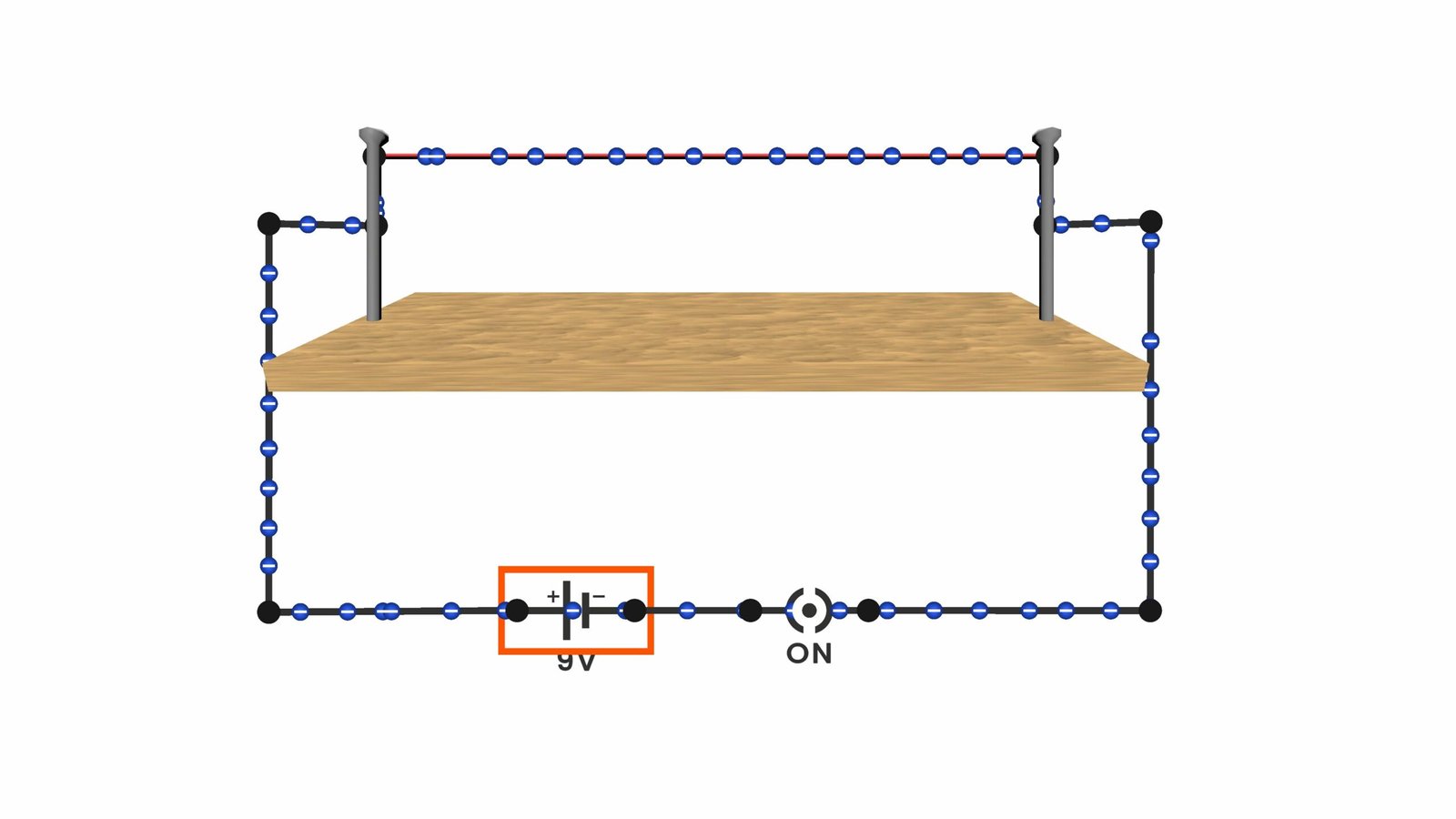
An electric fuse is a safety device that prevents damage to electrical circuits caused by excessive current. It works by melting and breaking the flow of electricity when the current becomes too high. The fuse contains a thin wire made from a material with a low melting point. Once the wire melts, the circuit opens, and the current stops — preventing overheating, fire, or damage to electronic devices.
Theory Behind How a Fuse Works
When electric current flows through a wire, it produces heat due to the resistance of the wire. The higher the current, the more heat is generated. Fuse wires are designed to melt when the heat exceeds a certain limit, cutting off the current.
Materials used for fuse wires are chosen based on their resistance and melting point:
- Copper is not a good fuse material because it has low resistance and does not heat up easily.
- Steel wool has high resistance, so it heats up and melts quickly, making it suitable.
- Tin and alloys (like Tin-Lead) are commonly used in real-life fuses because they have moderate resistance and melt safely at the required current level.
Fuses are rated as 1A, 5A, 10A, etc., depending on how much current they are designed to handle. When the current goes beyond the rated value, the fuse wire melts (blows) and disconnects the circuit.
Real-Life Uses of Electric Fuses
- Home circuits: Prevent fires and damage due to short circuits or power surges.
- Vehicles: Protect car electronics from overloading.
- Appliances: Found in TVs, chargers, refrigerators, and more to safeguard internal components.
Key Observations from the Experiment
- Fuse wires melt only when current exceeds a safe limit.
- Higher resistance materials melt faster than low resistance ones.
- Increased battery voltage raises current, causing the fuse to blow easily.
- Copper wires, even under high current, may not melt, making them unsafe for use in fuses.
Summary Table
| Material | Resistance Level | Behavior in High Current |
|---|---|---|
| Copper | Low | Does not melt, not suitable as fuse |
| Steel Wool | High | Melts quickly, suitable as fuse |
| Alloy (Tin-Lead) | Moderate | Commonly used in real fuses |
Explore Fuse Behavior with Dencity Virtual Science Lab
Understanding the working of a fuse is easier and safer with the Dencity app, a virtual science lab available on Android, iOS, and Desktop. Students can:
- Simulate a fuse circuit with different materials and currents.
- Adjust battery voltage and observe when the fuse melts.
- Test real-life situations like power surges or overloads.
- Learn about resistance, heat generation, and circuit protection in a hands-on, interactive way.
This experiment is part of the class 10 science curriculum and is perfect for helping students visualize why fuses are essential in our everyday lives.
Dencity for Teachers
With Dencity, teachers can promote interactive teaching and bring safety-based science into focus:
- Demonstrate fuse experiments live without the risks of handling real wires or batteries.
- Assign digital experiments with different fuse materials and voltage levels.
- Automatically track student progress and receive lab reports.
- Make learning more interactive and engaging with real-time feedback and simulations.
Works Seamlessly on Interactive Touch Panels
The Dencity virtual lab is fully optimized for interactive touch panels. Teachers can control circuit elements, adjust variables, and zoom into components with a simple touch — making science labs more accessible and immersive in classrooms.
Contact Us for Demos and Customized School Pricing
Want to integrate Dencity into your school’s science curriculum? Visit dencityapp.in to schedule a free demo or ask about custom pricing plans tailored for institutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the purpose of a fuse in an electric circuit?
To break the circuit and stop the flow of current if the current becomes too high, preventing damage. - Why doesn’t copper work as a fuse wire?
Because it has very low resistance and doesn’t heat up or melt easily under high current. - What materials are suitable for fuse wires?
Materials with higher resistance and lower melting points, such as tin, steel wool, or certain alloys. - What does a fuse rating mean?
It tells you the maximum current the fuse can handle before it melts, like 1A, 5A, or 10A. - How does increasing voltage affect the fuse?
Higher voltage increases current, which may cause the fuse to blow faster. - What happens if a fuse is not included in a circuit?
Without a fuse, excessive current can overheat wires, damage devices, or cause a fire. - Can fuses be reused?
No, once a fuse melts, it must be replaced. - Is this experiment safe to perform physically?
It involves current and heating — Dencity provides a safe virtual alternative. - Can students change materials and test different fuses in Dencity?
Yes, students can switch materials, adjust current, and observe behavior in real-time. - Where can schools get access to Dencity?
Visit dencityapp.in to request access, pricing, or a live demo.
Learn how circuits stay safe with Dencity — Your Virtual Science Lab for Interactive Learning.