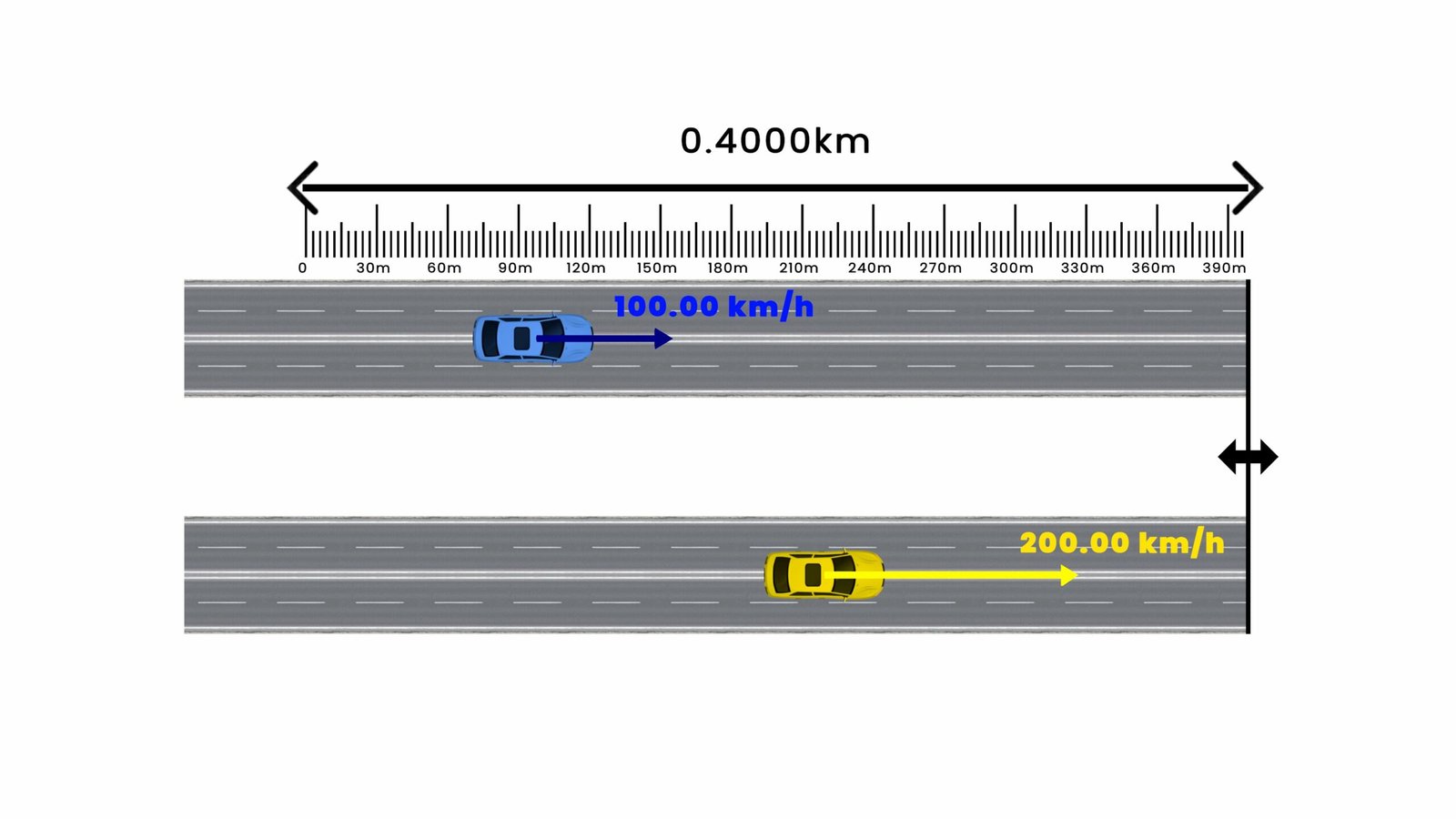
Speed Experiment – Understanding Motion and Time
Speed is a basic concept in physics that helps us understand how fast or slow something is moving. It tells us how much distance an object covers in a certain amount of time.
In simple words, if you want to know how quickly a car is moving, how fast a sprinter runs, or how soon a train will arrive — you are thinking about speed.
What is Speed?
Speed is the rate at which an object moves. It is calculated using this basic formula:
Speed = Distance / Time
This means, if something travels 100 meters in 20 seconds, its speed is:
Speed = 100 / 20 = 5 meters per second
Key Concepts:
- If you know speed and distance, you can find time: Time = Distance / Speed
- If you know speed and time, you can find distance: Distance = Speed × Time
Real Life Uses of Speed:
- Travel: Helps calculate how long it takes to reach a destination.
- Logistics: Delivery companies use speed to estimate arrival times.
- Sports: Measures athlete performance (e.g. runners, swimmers).
- Space Missions: Used to design paths and timings for rockets and satellites.
Observations:
- When speed increases, time decreases for the same distance.
- When speed decreases, time increases.
- Distance increases time when speed is fixed.
- Speed and time are inversely related — if one goes up, the other goes down (when distance is the same).
Summary Table:
| Scenario | Change in Speed or Distance | Effect on Time |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Distance | Speed increases | Time decreases |
| Fixed Distance | Speed decreases | Time increases |
| Fixed Speed | Distance increases | Time increases |
| Fixed Speed | Distance decreases | Time decreases |
Learn with Dencity – The Virtual Science Lab
Performing the Speed Experiment is easy and fun with the Dencity app — a powerful virtual science lab available on Android, iOS, and Desktop.
With Dencity, students from class 9 science and above can:
- Try real-time science experiments without needing physical tools.
- Get step-by-step calculations and live simulations.
- Understand concepts like speed, motion, and time visually and interactively.
Whether you’re a student or a teacher, Dencity brings science to life right in your classroom or home.
Dencity for Teachers
Dencity empowers interactive teaching by giving educators tools to:
- Demonstrate physics experiments in real-time.
- Assign experiments as homework with automatic tracking.
- Create virtual classrooms where students can explore and collaborate.
- Use interactive learning to help students understand abstract concepts like speed and motion.
This approach enhances engagement, especially for complex science topics.
Works Great on Interactive Panels
Dencity is fully compatible with interactive touch panels used in smart classrooms. Teachers can control variables, explain diagrams, and run full experiments using touch gestures — making learning more engaging and immersive.
Contact Us
Are you a school or institution? Reach out to us for customized pricing and demos to bring virtual science labs into your classrooms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is speed in simple terms?
Speed is how fast something moves — it shows how much distance is covered in a certain time. - How do you calculate speed?
Speed = Distance divided by Time. - What units are used for speed?
Common units are meters per second (m/s), kilometers per hour (km/h), or miles per hour (mph). - Can speed be zero?
Yes, if an object is not moving, its speed is zero. - What is the difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is how fast something is moving; velocity also tells you the direction of movement. - Why is speed important in real life?
It helps in travel, transportation, sports, and even space missions. - What happens when speed increases but distance is the same?
Time taken will decrease. - Is speed always constant?
No, speed can change based on how the object moves. - What tools are used to measure speed?
Speedometers in vehicles, GPS trackers, and timers. - How does Dencity help with learning speed experiments?
Dencity allows students to simulate experiments, change variables, and see real-time results, making the concept easier to understand.